Should You Take An Early Retirement?
The story is a common one these days. You have been furloughed or laid off, just a few years before you plan to retire. Or, your work-from-home arrangement is ending, and you’re not keen on resuming the commute or going back to a crowded workspace. Retiring early may be a good idea, since fate has presented the opportunity?
Many 50- and 60-somethings are asking themselves this very question. In fact, the average American retires at age 61.1 But, that’s at least five years away from collecting full Social Security retirement benefits, not to mention pensions, which typically begin at age 65, when available. What’s more, Medicare coverage does not begin until age 65, leaving early retirees with potentially hefty health insurance premiums until Medicare kicks in.
Anyone contemplating retiring early will want to plan carefully and ask several important questions.
When Should You Begin Collecting Social Security?
You can begin collecting Social Security retirement benefits as early as age 62. But you will face a significant reduction if you start before your normal retirement age: from 66 to 67, depending upon when you were born. Those choosing to collect before that age face a reduction in monthly payments by as much as 30%. Also, there is a stiff penalty for anyone who collects early and earns wages in excess of an annual earnings limit ($18,240 in 2020).
What age is best for you will ultimately depend upon your financial situation as well as your anticipated life expectancy. For most people, holding off until normal retirement age is worth the wait. But you may want to consider taking your benefits earlier if:
- You are in poor health.
- No longer working and need the benefit to help make ends meet.
- Earn less than your spouse and your spouse has decided to continue working to help earn a better benefit.
How Will You Fund Health Care Costs?
A big obstacle to early retirement is health insurance. If you are working for a company that pays all or most of your health insurance, you could face hundreds of dollars in added monthly expenses if you retire before age 65. Plus, most companies no longer offer retiree health benefits, and if they do, the premiums can be high or the coverage low. In addition to health insurance premiums, there are also co-pays, annual out-of-pocket deductibles, uncovered procedures, and out-of-network costs to consider — not to mention dental and vision care costs.
On the positive side, the Affordable Care Act (ACA) prohibits insurance companies from discriminating because of preexisting illnesses and limits how much they can charge based on age. And for those with lower incomes, government subsidies may be available.
What Will Early Retirement Mean for Your Investing and Withdrawal Strategies?
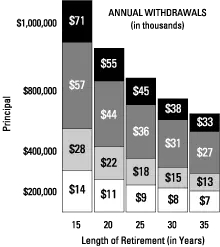
Perhaps the most significant concern for early retirees — one that is often overlooked — is how retiring early will impact their investing and withdrawal strategies. Retiring early means taking larger distributions from your retirement savings in the early years until Social Security and pension payments begin. This can have a significant impact on how long your savings last, perhaps more so than if larger distributions are taken later in retirement. Consider the following:
- Delay withdrawals from tax-favored retirement accounts, such as individual retirement accounts (IRAs) or 401(k) plans. The longer you wait to withdraw this money, the more you can potentially benefit from tax-deferred compounding. Instead, consider tapping into taxable accounts first.
- Adjust your withdrawal rate to help ensure that your savings will last throughout a lengthened retirement. Financial planners typically recommend a 4%-5% annual withdrawal rate at retirement, but you may want to lower this since you will need your savings to last longer.
- Structure your investments to include a significant growth element. Since your money will have to last longer, you will want to consider including stocks or other assets that carry high growth potential. Stocks are typically more volatile than bonds or other fixed-income investments but have a better long-term record of outpacing inflation.
So, if the coronavirus pandemic has left you thinking about retiring early, make sure you are prepared. The first place to start is with a detailed plan that includes estimated income and expenses. Work with a financial professional to put in place a plan that factors in all of the necessary elements you will want to consider.
Source/Disclaimer:
1Source: Gallup, Snapshot: Average American Predicts Retirement Age of 66, May 10, 2018.
This material was prepared by LPL Financial. This material is for general information only and is not intended to provide specific advice or recommendations for any individual. There is no assurance that they views or strategies discussed are suitable for all investors or will yield positive outcomes. Investing involves risks including possible loss of principal. Any economic forecasts set forth may not develop as predicted and are subject to change. All performance referenced is historical and is no guarantee of future results.